In farms of any size to large losses leads Colienterotoxemia, Which is also called Swelling of piglets.
Description
Colienterotoxemia(A disease of a "good host") is an acute infectious disease of pigs characterized by impaired central nervous system function, enterotoxemia and the formation of edema in various organs and tissues.Lethality in the absence of treatment can be up to 100%.
Pathogen of the disease
Enteropathogenic and hemolytic serovariants of Escherichia coli.
The bacteria are sufficiently stable in the external environment: in the soil, water, pus, livestock premises can preserve vital activity for 1-2 months. At a temperature of 70 ° C, the Escherichia collapse after 15-20 seconds.
Factors that contribute to the development and spread of the disease
- Stress when absent;
- A sharp change in the type of food from the sow's milk to mixed fodder of vegetable origin (no additional feeding with pre-feed mixed suckling piglets);
- Unbalanced by the amount of protein or its excessive amount in the diet of piglets;
- Excessive and infrequent (less than 2 times a day) feeding of weaned piglets with dry food;
- Sharp transition from pre-launch mixed feed to start (less than 3 days);
- Low temperature in the room for weaned piglets (less than 25-27 ° C);
- Feeding spoiled or moldy fodder;
- Violation of the technology of mixing and preparation of mixed fodders.
All these factors cause a violation of gastric motility, intestinal peristalsis, a delay in normal defecation and the formation of products of incomplete protein breakdown, which leads to a rapid multiplication of Escherichia in the digestive tract.
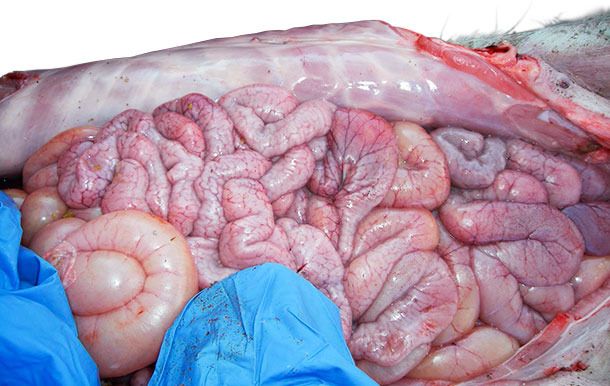
Necrosis of the small and large intestine
The products of the life activity of the Escherichia cause a general intoxication of the organism, affecting various organs and tissues.
Clinical signs of swelling of piglets
The disease occurs in three forms:
- Super-fast (lightning fast);
- Acute;
- podostraя.
OvergrownThe flow is observed in pigs with good fatness. Animals suddenly die within 2-3 days without obvious clinical signs.
AcuteThe course for the edematous disease is the most common. The disease lasts from a few hours to 2-3 days.
PodostroeCurrent is more often seen in pigs of older age groups. The most characteristic sign of edema of the eyelids (not in all animals) and conjunctivitis. Sometimes swelling also manifests itself in the area of the nome, patch, and pharynx. Duration of the disease - 5-7 days. In the subacute course of the disease, recovery is possible.

Classic features of Otecki
There are also four forms of manifestation of the disease:
- Intestinal;
- Edematous;
- Nervous;
- Mixed.
Intestinal form is manifested in piglets of medium and below average fatness and is characterized by symptoms of digestive function disorders - depression, a slight increase in body temperature to 40.3-41.1 ° C, diarrhea, which often turns into constipation. Sometimes noted vomiting and bloating.
Edema form manifested in well-fed piglets and is characterized by general weakness, conjunctivitis, edema of the eyelids, subcutaneous tissue in the head, chest, abdominal wall. The duration of the disease is 1-3 days. Almost all the sick piglets die.
Nervous shape characterized by symptoms of the central nervous system - depression, which is replaced by a sharp excitement, a tense staggering gait, maneuvers and attempts to move forward. Appears epileptic seizures, the body temperature decreases trembling in the muscles, paresis, and paralysis of the limbs, convulsive contractions. The head is often thrown back. Epileptic seizures do not last long and are repeated until death.
When Mixed form observed symptoms of lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system and edema of the eyelids. Most sick pigs die in 6-8 hours.
Treatment
It is believed that treatment can be effective only at the onset of the disease before the development of the nerve symptom complex.
Sick animals are isolated, kept one day on a starvation diet without limiting access to water. Disposable Glauber's salt is given (25-30 grams). The next 5-7 days 30-50% reduce the yield of mixed fodder.
Zinc oxide is used at a dose of 3-5 kg per ton of mixed feed for 5-7 days and antibiotic therapy (amoxicillin or apramycin), sulfonamides (colistin, etc.).
Prevention
Prevention should be aimed at eliminating adverse factors:
- Balanced full-rationed rations for sows and pre-starter mixed fodder in composition as close as possible to milk;
- Compliance with sanitary and hygiene and zootechnical norms for keeping pigs after weaning;
- Low protein recipes for animal feed;
- Control homogeneity of mixing andThe size of the mixed feed;
- Daily monitoring of animals.




