Nodular dermatitis of cattle- an infectious virus disease mainly of highly productive cultivated breeds of cows and zebu, caused by a DNA-containing virus closely related to the smallpox virus.
The disease is characterized by a short-term fever, a lesion of the skin, lymphatic system, mucous membranes, with the formation of tubercles in the subcutaneous tissue and their necrosis, a sharp decrease in milk secretion, infertility and malnutrition.
Prevalence
The disease originated on the African continent, where in 1929 was first registered.At the moment, the disease is registered in Russia, Bulgaria, Hungary, Austria, Armenia, Kazakhstan.
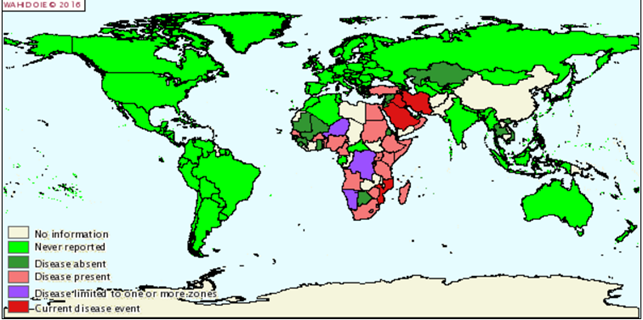
Карта распространения нодулярного дерматита КРС январь-июнь 2015
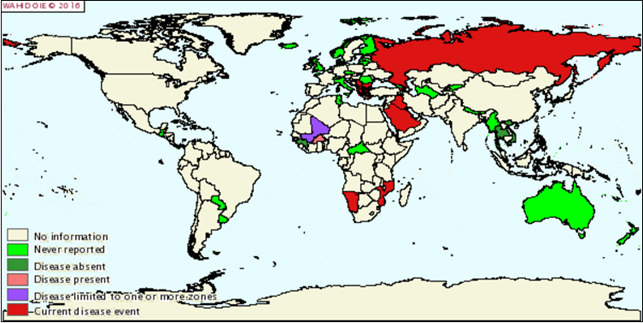
Карта распространения нодулярного дерматита КРС январь-июнь 2016
Epizootology
The source of the virus is sick animals and virus carriers. Isolation of the virus occurs in the epithelium and the contents of the pustules of the skin and mucous membranes. Find the causative agent in urine, semen and other secrets.
Nodular dermatitis is transmitted to animals mainly by transmissible transmission through bloodsucking insects. The virus can carry birds.
The spread of infection between livestock farms occurs with direct contact through care items, feed.
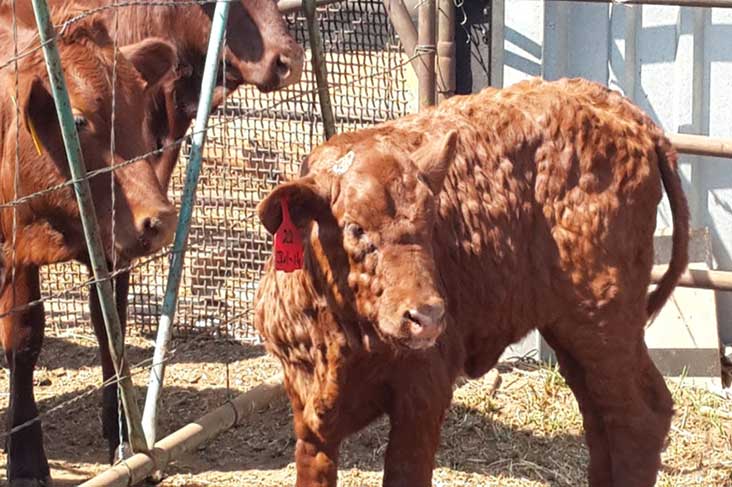

Распространение инфекции между поголовьем фермы
Mortality in this disease does not exceed 10%, but the economic damage is significant, as the dairy productivity decreases, the sexual cycle is disrupted, infected abortions are observed in infected pregnant cows, sex sterility develops in bulls of producers. Depletion of sick animals can last a long period.The incubation periodCan last from 3 to 30 days, nodular dermatitis does not manifest itself in any way, the animals are not isolated, so the risk of spread of infection increases.
The disease can manifest itself in two forms: Acute and Chronic. Also known Atipical Nodular dermatitis.
When Acute form The diseased animal rises sharply body temperature (up to 40 degrees). In this case, the animal's appetite decreases, tears flow and mucus discharge from the nose appears.
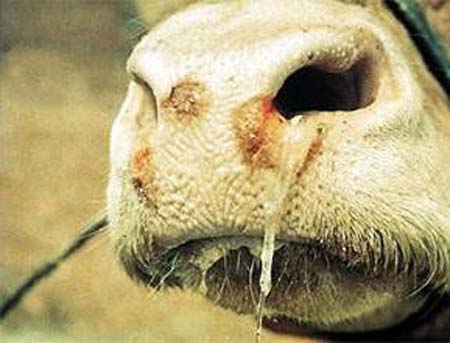
Слизистые выделения из носа
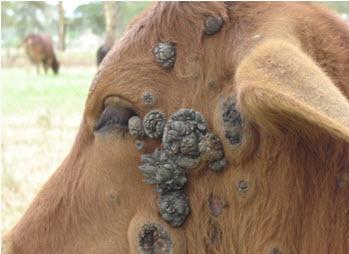
Two days later, nodules with a diameter of 0.5 to 7 cm and a height of up to 0.5 cm are formed on the skin of the animal. The number of them can vary from 10 to several hundred. In some cases, they merge. The nodules are dense to the touch, after a few hours the epidermis begins to peel off along their contours. In this case, a fovea is formed in the center of each nodule. Necrosis begins to spread from it.
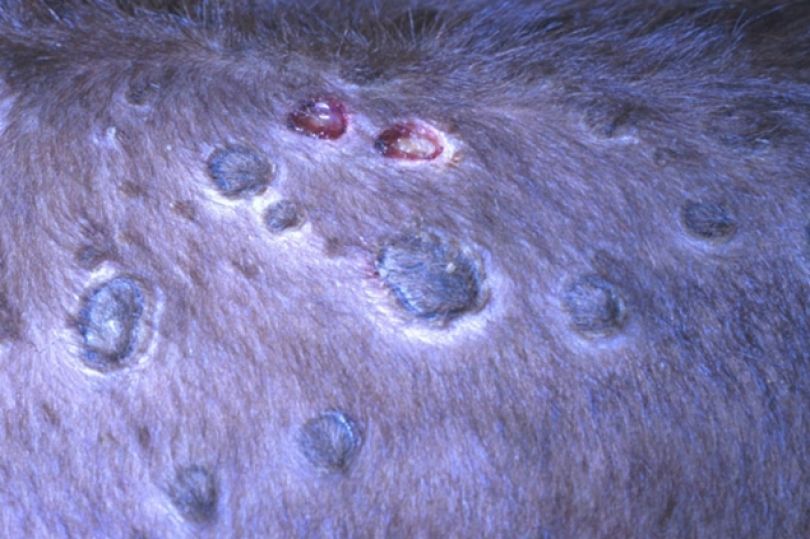
Начало распространения некроза
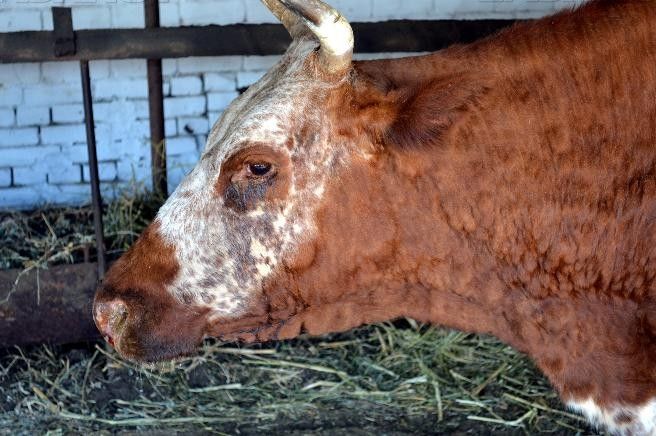
The affected areas are fringed by a roller of granulation tissue up to 3 mm wide. After a week, the necrotic area, which has the shape of a cylinder about 1 * 2 cm in size, dries up and disappears. Later, the cavity formed on the animal's skin is filled with tissue and overgrown with pigment-deprived skin with hair. ButOccurs only in the absence of complications.
Заросший участок лишенной пигмента кожи и шерсти
It also happens that ulcers form on the skin of the animal. Some nodules can not dry out for a year or more.
In addition to skin formations,Nodular dermatitis of bovine animals is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Pink color of milk, it surrenders very hard - drop by drop. When heated, the milk of the infected animal acquires a gel-like appearance.Feeding it to calves can be done after pasteurizationAt a temperature of 85 degrees for half an hour.
- Exhaustion of the animal due to loss of appetite;
- The appearance on the centuries of a cow or bull of sores or erosion;
- Current saliva from the mouth and purulent fetid mucus from the nose;
- Blurred cornea and decreased vision in the animal.
Pathological changes
On a section of the tubercles, a connective tissue of white-gray color, of a dense consistency is found, the skin and subcutaneous tissue are impregnated with a serous reddish liquid.

Некротизированные бугорки
Necrotized tubercles contain caseous masses, under which are formed sores. The tubercles are also found between the muscle fibers, in the lungs, abomasum, cicatrix, uterus. On the pleura, heart, liver, hemorrhage.

В начальной стадии болезни эпителиальные клетки увеличены и в них появляются вакуоли
Histomorphological changes depend on the stage of development of the process. In the initial stage of the disease, epithelial cells are enlarged and vacuoles appear in them. In the histophoresis of the tubercles, cytoplasmic inclusions of a round or oval shape are often often larger than the nucleus. These inclusions are found in epithelial cells and histiocytes.
Diagnosis
Determine the infection based on the overall clinical picture and laboratory diagnosis of the disease.
Symptoms of nodular dermatitis are similar to manifestations of hives, dermatophileosis, smallpox, demodectic and lymphongitis.
Sometimes this disease is confused even with banal insect bites, so when there are any nodules on the skin of animals, it is necessary to conduct laboratory studies.
Preventive measures and control measures
Specific methods of treatment are not developed. Natural recovery occurs in 90% of cases. Symptomatic treatment is used. The animals are provided with good conditions for feeding, keeping.




